Cocaine in the Blood Stream
The onset and intensity of cocaine’s effects can depend on how a person ingests the drug and what route it takes to enter the bloodstream. Once a person has cocaine in the blood, these effects are typically brief – but someone may test positive on a blood test long after the drug’s effects have subsided.
How Does Cocaine Enter the Bloodstream?
Cocaine can enter the bloodstream in multiple ways:
- The most direct manner is to inject the drug directly into a vein.
- Smoking cocaine (or crack) is the second quickest way to get cocaine in the blood, as the lungs have a large surface area through which the drug can pass into the bloodstream.
- If someone snorts cocaine, the drug will pass from specialized cells in the nasal membrane to capillaries that will distribute it throughout the bloodstream.
- Oral ingestion is the slowest way to get cocaine in the blood. When someone swallows cocaine, the drug must pass through the stomach and liver before being sent to the central nervous system via the bloodstream.
How Long Does Cocaine Stay in Your Blood?
There’s no precise answer to the question of how long cocaine will remain in your bloodstream.
Typically, cocaine can stay in your blood anywhere between seven hours and two days. However, the exact length of time that you may continue to have cocaine in the blood can vary depending on several factors, including your metabolism and how much cocaine you have been using.
The half-life of cocaine is about 90 minutes. Half-life refers to the amount of time it takes for half of a substance to be eliminated from the body. It usually takes four to five half-lives for a substance to fall below the detectable limit. For cocaine, this means that it could take about seven and a half hours for the drug to be eliminated.
However, during the process of breaking down cocaine in order to eliminate it, your body converts the drug into compounds called metabolites. The half-life of cocaine metabolites can be as long as 7.5 hours. This means they may still be detectable in your bloodstream for about two days.
Does Cocaine Cause High Blood Pressure?
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is one of the many dangers of cocaine abuse. As described in an April 2014 study in the open access peer-reviewed journal PLOS One, cocaine’s impact on the heart can cause a variety of problems, including “accelerated hypertension, acute myocardial ischaemia and infarction, aortic dissection, and life-threatening arrhythmias.”
The researchers who conducted the 2014 study did not limit participation to individuals who were receiving treatment for cocaine addiction. Thus, their findings suggest that even people who consider themselves to be “casual” or occasional recreational users of cocaine are also at risk of high blood pressure and other heart-related concerns.
What Other Dangers Does Using Cocaine Pose?
The harmful effects of having cocaine in the blood extend far beyond heart-related matters. People who abuse this substance expose themselves to a wide range of negative outcomes, including physical, psychological, and social impairments.
Depending on the amount and frequency of a person’s cocaine use, as well as the ways they ingest the drug, potential dangers include:
- Damage to the nasal septum
- Breathing problems
- Bleeding in the brain
- Malnutrition
- Elevated risk of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C
- Sexual dysfunction
- Anxiety, paranoia, and other mental health concerns
- Job loss and long-term unemployment
- Financial devastation
- Ruined relationships
- Being arrested and incarcerated
- Addiction, overdose, and death
The severity of these effects underscores the importance of getting appropriate professional help if you have become addicted to cocaine. With proper care, you can end your abuse of this dangerous drug and build a healthier life in recovery.
Do Cocaine Blood Tests Always Work?
The reliability of cocaine blood tests depends on the quality of the collection procedure and the accuracy of the system that conducts the screening. In most cases, tests for cocaine in the blood are highly effective. When a person has ingested cocaine within the previous 48 hours, there’s a good chance that they will test positive on a blood screening.
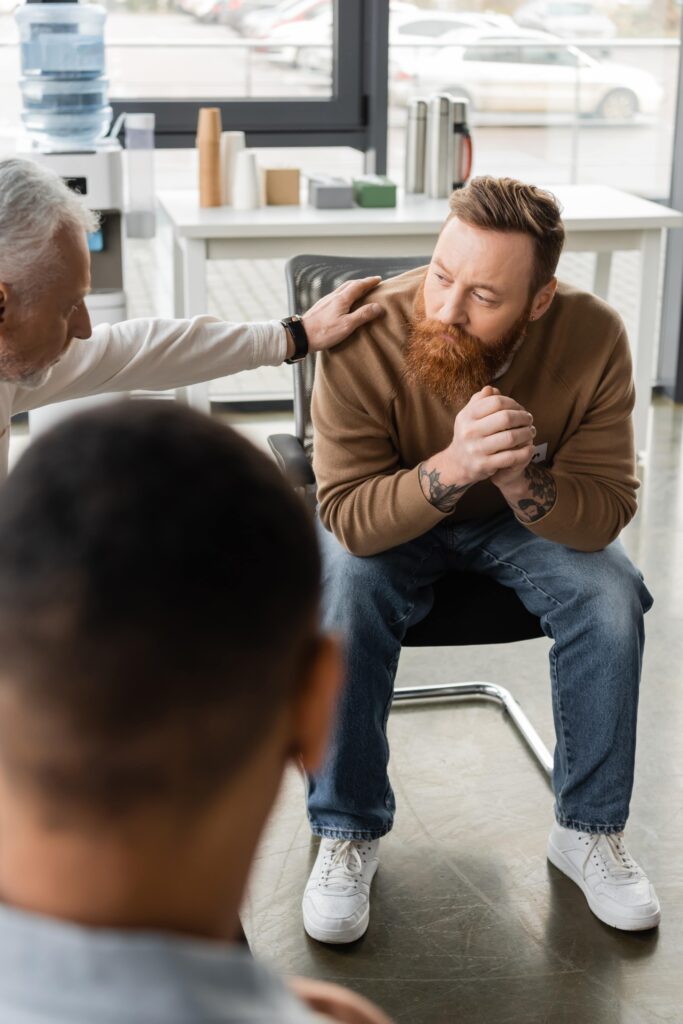
If You Have An Addiction To Cocaine
If you’ve developed an addiction to cocaine, you might feel like there’s no escape, or that no one could possibly understand what you’re going through.
These thoughts are normal and common. They’re also wrong.
Don’t believe the lies that your addiction is telling you. Don’t allow this disease to undermine your faith in yourself, skew your judgement, and isolate you from the people who care most about you.
Here’s the truth: Your path toward a healthier and more hopeful future may be much closer than you realize. With one phone call, you can find the proper cocaine treatment that may literally save your life.
Here are just a few of the many reasons why you should make that call today:
- Cocaine addiction is a chronic, progressive disease. This means that, in the absence of appropriate care, your problem is likely to only get worse.
- The distress of cocaine withdrawal can keep you trapped in the chains of active addiction. When you get professional care, you can begin your treatment in a detox program. This is where a team of experts can provide both medical and therapeutic support to help keep you safe and as comfortable as possible while you complete withdrawal.
- Therapy can help you identify and address any co-occurring mental health concerns or underlying issues that may have contributed to your struggles with cocaine. This can be vital for the success of your recovery efforts.
- During treatment, you can develop skills and strategies for responding to triggers, managing stress, resolving conflicts, and dealing with other common challenges without resorting to substance abuse.
- Treatment can introduce you to the power of sharing support with other members of the recovery community. Developing a strong personal support network can be essential for successful recovery.
Contact Our Cocaine Detox and Rehabilitation Center in California
If you or someone that you care about have become addicted to cocaine, Sanctuary Treatment Center is here to help. Our cocaine detox and rehabilitation center in southern California is a safe and welcoming place where you can receive personalized services from a team of highly skilled and compassionate professionals.
Our continuum of care includes detoxification, residential rehab, outpatient programming, and aftercare planning. We can meet you wherever you are in your recovery journey, then develop the customized plan to get you where you want to be.
Don’t let cocaine addiction rob you of one more day. To learn more about our services, or to schedule a free assessment, please visit our Contact Us page or call us today!